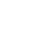What is a Diaphragm Pump and How Does it Work in Applications
Diaphragm pumps are essential in various industries, offering versatility and efficiency. According to John Smith, a renowned expert in the 2 diaphragm pump sector, "These pumps are the backbone of fluid handling." Understanding their function and applications is crucial for maximizing their benefits.
A diaphragm pump operates by creating a vacuum, pulling fluid into the chamber through the diaphragm's movement. This simple yet effective mechanism allows for precise fluid transfer. It is particularly helpful in applications requiring gentle handling of shear-sensitive materials. However, some users notice limitations in pressure output, leading to challenges in high-demand environments.
Real-world performance shows that diaphragm pumps can struggle with abrasive fluids, which can wear out the diaphragm sooner than expected. Regular maintenance is vital to prevent downtime. Understanding these nuances can lead to improved efficiency and longevity of the 2 diaphragm pump in various applications.
What is a Diaphragm Pump?
A diaphragm pump is a type of positive displacement pump. It uses a flexible diaphragm to move fluids. As the diaphragm moves back and forth, it creates a change in volume inside the pump chamber. This action draws fluid in and pushes it out. It’s a simple yet effective mechanism.
These pumps are commonly used in various applications. They handle viscous liquids, slurries, and even corrosive fluids. The design allows for a wide range of flow rates. They can be used in industries like food processing and chemical manufacturing. However, diaphragm pumps can be prone to wear over time. Regular maintenance is essential to avoid issues.
One notable feature is their ability to run dry without damage. This makes them versatile, but it raises questions. What if the diaphragm ruptures? The consequences can be messy and costly. Users must regularly check for leaks. Every application may have unique challenges to consider. Understanding the specific needs is crucial for optimal performance.
Principles of Operation in Diaphragm Pumps
Diaphragm pumps are unique devices widely used in various applications. They operate on the principle of a flexible diaphragm that alternately compresses and releases to move fluids. This mechanism is fascinating yet straightforward.
When the diaphragm moves up, it creates a vacuum that draws fluid into the pump chamber. Once the chamber fills, the diaphragm moves down, pushing the fluid out of the discharge outlet. This back-and-forth motion is driven by either air pressure or an electric motor. The design often includes check valves, ensuring fluid flows in one direction only. However, the efficiency might vary based on application and setup.
It's essential to consider the material compatibility. Not all fluids are suitable for every diaphragm pump. For instance, corrosive substances could damage the diaphragm, leading to leaks. Regular maintenance checks can help prevent these issues, but they require time and diligence. Understanding these operational principles sheds light on both the potential and limitations of diaphragm pumps in real-world scenarios.
Common Applications of Diaphragm Pumps

Diaphragm pumps are versatile tools widely used across various industries. They are ideal for transferring fluids, especially viscous or abrasive materials. A diaphragm pump can handle slurries easily, making it popular in wastewater treatment plants. They excel in applications where contamination must be avoided since they are designed to pump liquids without direct contact.
In the agricultural sector, diaphragm pumps play a critical role. Farmers use them to deliver fertilizers and pesticides with precision. This ensures an even distribution, which is crucial for crop yield. The pumps can also manage water efficiently in irrigation systems. However, they may occasionally struggle with certain chemical agents, requiring adjustments in material choice for longevity.
In the food and beverage industry, diaphragm pumps maintain hygiene standards. They transport liquids like juices and sauces without risking contamination. Yet, they can be sensitive to harsh cleaning processes. Regular maintenance is essential to avoid performance issues. These pumps embody both versatility and challenges, requiring careful consideration in their application.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Diaphragm Pumps
Diaphragm pumps are widely used in various industries. They have specific advantages that appeal to many users. One key benefit is their ability to handle abrasive and viscous fluids. This makes them suitable for a range of applications, from chemical processing to food and beverage production. Their design allows for self-priming, which reduces the need for additional equipment. The low maintenance requirement is also attractive. Users can often rely on them for extended periods without significant downtime.
However, diaphragm pumps are not without drawbacks. They can experience pulsation issues, which may affect fluid flow consistency. This can be a concern in applications that require precise flow rates. Additionally, diaphragm wear can lead to failures. While replacements are straightforward, they can disrupt workflow. The initial cost of diaphragm pumps can also be higher compared to other types. For some, this may deter them from choosing this option.
Overall, while diaphragm pumps offer various advantages, they present challenges too. Users must weigh these pros and cons carefully. Each application may call for different considerations, and it’s essential to reflect on specific needs.
What is a Diaphragm Pump and How Does it Work in Applications - Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Diaphragm Pumps
| Dimension | Description |
|---|---|
| Type | Positive displacement pump |
| Working Principle | Uses a diaphragm to create a vacuum and draw fluid in |
| Applications | Chemical transfer, water treatment, food processing |
| Advantages | Self-priming, can handle viscous fluids, minimal contamination risk |
| Disadvantages | Limited flow rates, potential for diaphragm wear, maintenance required |
| Materials Used | Rubber, Teflon, PVC, metals for pump casing |
| Maintenance | Regular inspection of diaphragm, seals, and fluid paths |
Maintenance Tips for Diaphragm Pumps
Diaphragm pumps are efficient at transferring liquids and slurries. To ensure they operate effectively, regular maintenance is essential. A crucial tip is to inspect the diaphragm for wear. Over time, materials can degrade. This affects performance. A small crack can lead to significant leaks. Always check the diaphragm during routine inspections.
Cleaning the pump frequently is another key step. Dust and debris can clog the system. Use compressed air to clear out any buildup. It’s also important to monitor the valves. A malfunctioning valve can cause pressure issues. Replace them if you notice any signs of damage or fatigue.
Don’t overlook lubrication. Proper lubrication keeps the moving parts functioning smoothly. However, too much oil can create problems. Striking a balance is vital. Keeping a maintenance log can help track the pump's condition. If issues constantly arise, reconsider the application. Sometimes, a different type of pump might be a better fit.
Diaphragm Pump Applications and Maintenance Frequency
This bar chart illustrates the frequency of maintenance tasks for diaphragm pumps based on various applications. It highlights the importance of regular upkeep tailored to specific operational settings.
Related Posts
-
Top 10 Diaphragm Pump Applications for Efficient Fluid Transfer
-
Unlocking the Science: How Pneumatic Diaphragm Pumps Revolutionize Fluid Transfer Efficiency
-

Understanding the Advantages of Pneumatic Diaphragm Pumps in Industrial Applications
-
How to Choose the Right Air Operated Double Diaphragm Pump for Your Needs
-
What is a 55 Gallon Hand Pump and How Does it Work Tips and Uses
-

Top 5 Benefits of Using a Barrel Hand Pump for Efficient Liquid Transfer
 |
Need Help? Call Us 203-740-1877 
|
We're ready to help identify, size and spec your pumps, filters |
All Products
Reliable Equipment Sales, LLC
Pumps, Parts, and Equipment – Guidance Included
103 Hempel Drive
Wolcott, CT 06716
Telephone: 203-740-1877
Toll Free Fax: 866-523-1693
Email: sale@rewritertool.com